Exploring Remote Operation’s Role In Making Offshore Energy Greener
The offshore energy industry is under increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices and reduce its carbon footprint due to growing concerns about climate change and the need to transition toward cleaner energy sources. Remote operations technologies and methods have emerged as a crucial solution to this challenge, enabling operators to remotely access, control, inspect, and repair energy systems in offshore locations. By reducing the need for on-site personnel and equipment, remote operations can help minimize the environmental impact of offshore energy production and support the transition towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. In this article, we will explore how remote operations technology is playing a pivotal role in making offshore energy greener.
Photo credit: Fugro
What are Remote Operations for Offshore Energy?
Remote operations for offshore energy involve technology and communication networks to remotely monitor, control, and maintain offshore energy assets from onshore locations. This includes offshore platforms, pipelines, and other infrastructure for oil and gas production and renewable energy (wind, wave, tidal, and solar).
Photo credit: Offshore Wind Farm Foundation, Nigg Energy Park
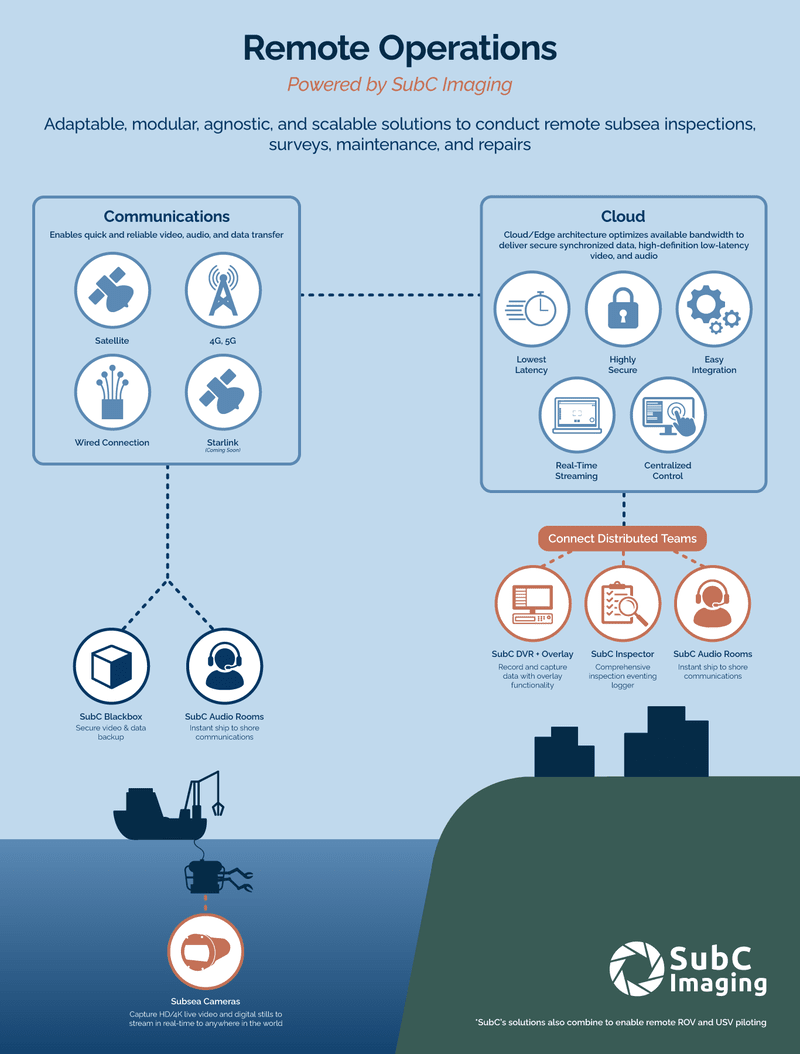
What Technologies Enable Remote Operations?
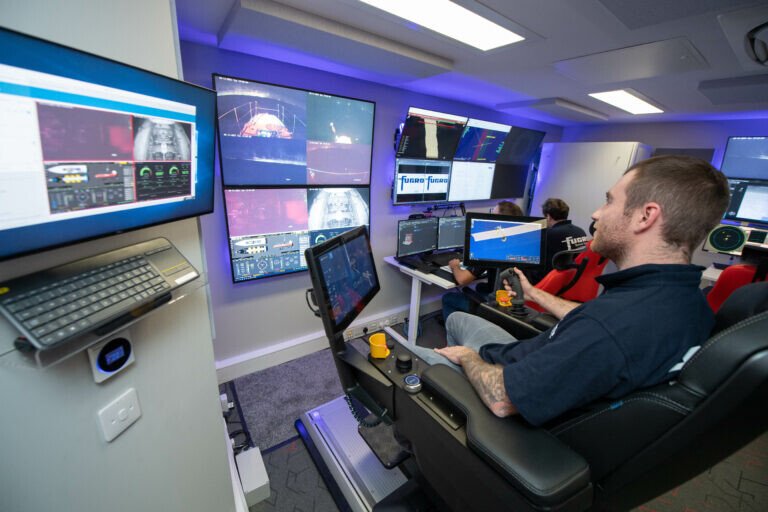
Remote operations combine technologies to enable remote monitoring and control of offshore operations from an onshore location. The technology is highly dependent on the application, but common technologies include deep-sea cameras, ROVs, fiber-optic communication, satellite communication, real-time control software, and real-time streaming.
Deep-sea cameras, like those designed and manufactured by SubC, are designed to withstand harsh underwater environments and provide high-quality video footage. This footage can be streamed live anywhere in the world, allowing operators to remotely monitor the performance of offshore installations without the need for complex infrastructure or equipment. Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) are underwater robots that can be remotely controlled and equipped with cameras and sensors, allowing them to perform tasks such as maintenance and repair.
Effective communication is essential for remote operations, and fiber-optic communication and satellite communication are two key technologies used to establish reliable and secure communication over long distances. Real-time control software allows operators to remotely monitor and control offshore operations from an onshore location, providing real-time data on the environment and equipment. The software can also control equipment and perform tasks such as maintenance and repair. Real-time streaming and DVRs, black-boxing, data routing, and audio chat also enable remote operations by providing a comprehensive solution for data recording and analysis, vehicle control, instant communication, and enhanced safety.
How Do Remote Operations Help Reduce Offshore Energy’s Carbon Footprint and Environmental Impact?
Remote operations in the offshore energy industry can lower the carbon footprint and environmental impact in several ways:
Reducing Transportation
Remote operations can eliminate the need for employees to travel to offshore facilities and locations. Traveling to and from offshore platforms requires helicopters or boats, which consume significant fuel and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Optimizing Operations
Another benefit of remote operation technology is that it can improve the efficiency of offshore energy production. By allowing for real-time monitoring and control of operations, operators can quickly identify and address issues that may impact production. This helps reduce downtime and improve the overall productivity of offshore platforms.
Reducing Energy Consumption
Remote operations can allow for real-time monitoring of energy usage, which can help identify areas of inefficiency and optimize energy consumption. The result is significant reductions in carbon emissions associated with energy consumption.
Eliminating The Need For Permanent Facilities
Remote operations can eliminate the need for permanent offshore facilities, such as living quarters and support infrastructure. This can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with the construction, operation, and maintenance of these facilities.
Efficiency and Reliability
Remote operations technologies are also helping to improve the efficiency and reliability of traditional offshore energy sources, such as oil and gas. By using predictive analytics tools and advanced sensors, companies can identify and address potential issues in offshore platforms and pipelines before they escalate into major problems. This reduces the risk of costly downtime and minimizes the environmental impact of offshore energy operations.
Additionally, as energy storage solutions become increasingly vital in the offshore energy industry, remote operation technologies enable companies to design and test new energy storage systems more quickly and efficiently. By reducing the time and cost necessary to introduce these systems into the market, renewable energy becomes more dependable and economical.
Remote Operations and the Development of Renewable Energy Sources
Photo credit: Burbo Bank Offshore Wind Farm
Developing renewable offshore energy sources, such as wind and tidal power, relies heavily on remote operations. These energy sources require specialized equipment, often located in challenging and remote locations. Using remote operations, operators can monitor and control this equipment in real-time, ensuring it operates safely and efficiently.
For example, in the case of offshore wind energy, remote operations are used to monitor and control the operation of wind turbines, which can be located far from shore in harsh and challenging environments. By using real-time monitoring and control systems, operators can optimize energy production, ensuring that the turbines capture as much energy from the wind as possible while minimizing downtime.
Conclusion
In conclusion, remote operation technologies have the potential to play a significant role in making offshore energy production greener. By reducing the need for human intervention offshore, improving the efficiency of operations, and minimizing environmental impacts, the technology can help the industry reduce its carbon footprint and operate more sustainably. As the industry continues exploring new technologies and methods to improve its environmental performance, remote operation technology will likely become an increasingly important tool for offshore energy production.